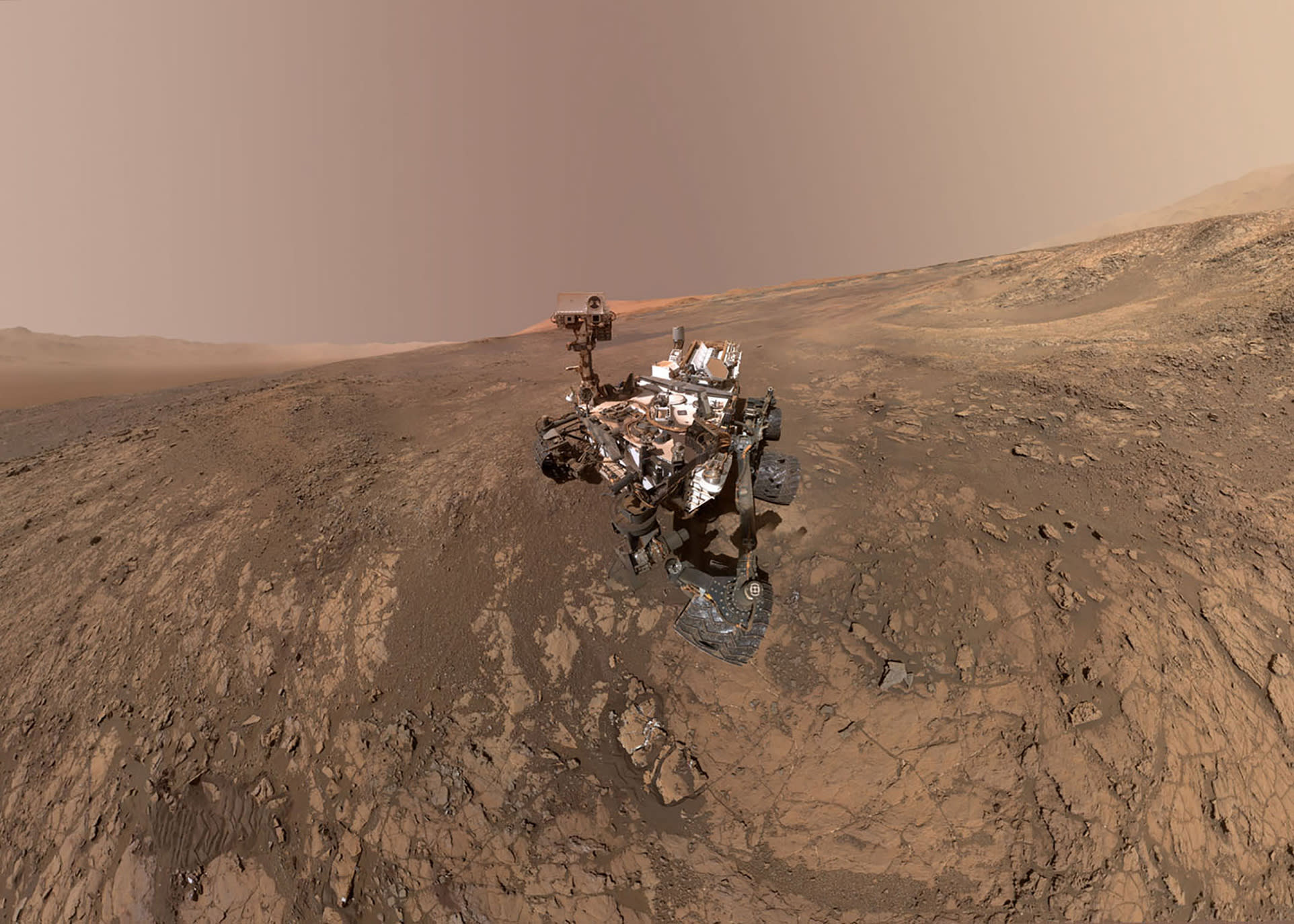


Learning more about Martian gravity and how terrestrial organisms fare under it could be a boon for space exploration and missions to other planets as well. Naturally, they also claim that their astronauts will be "well prepared with a scientifically valid countermeasures program that will keep them healthy, not only for the mission to Mars, but also as they become adjusted to life under gravity on the Mars surface." What these measures are remains to be seen. Their proposed mission calls for many months in space to get to Mars, and for those volunteering to spend the rest of their lives living on the Martian surface. Citing a recent study of International Space Station (ISS) astronauts, they acknowledge that mission durations ranging from 4-6 months show a maximum loss of 30% muscle performance and maximum loss of 15% muscle mass. Credit: Bryan Versteeg/Mars Oneįor example, crowd-sourced projects like Mars One make allowances for the likelihood of muscle deterioration and osteoporosis for their participants. Basically, the effects of long-term exposure to gravity that is just over one-third the Earth normal will be a key aspect of any plans for upcoming manned missions or colonization efforts.Īrtist’s concept of a Martian astronaut standing outside the Mars One habitat. Understanding Mars' gravity and its affect on terrestrial beings is an important first step if we want to send astronauts, explorers, and even settlers there someday. However, ongoing research into the effects of microgravity on astronauts has shown that it has a detrimental effect on health – which includes loss of muscle mass, bone density, organ function, and even eyesight. Based on the Earth's own surface gravity, this works out to an acceleration of 3.711 meters per second squared.Īt present, it is unknown what effects long-term exposure to this amount of gravity will have on the human body. The surface gravity of Mars can therefore be expressed mathematically as: 0.107/0.532², from which we get the value of 0.376. It also has a mean radius of 3,389.5 km, which works out to 0.532 Earth radii. Credit: įor instance, Mars has a mass of 6.4171 x 10 23 kg, which is 0.107 times the mass of Earth.
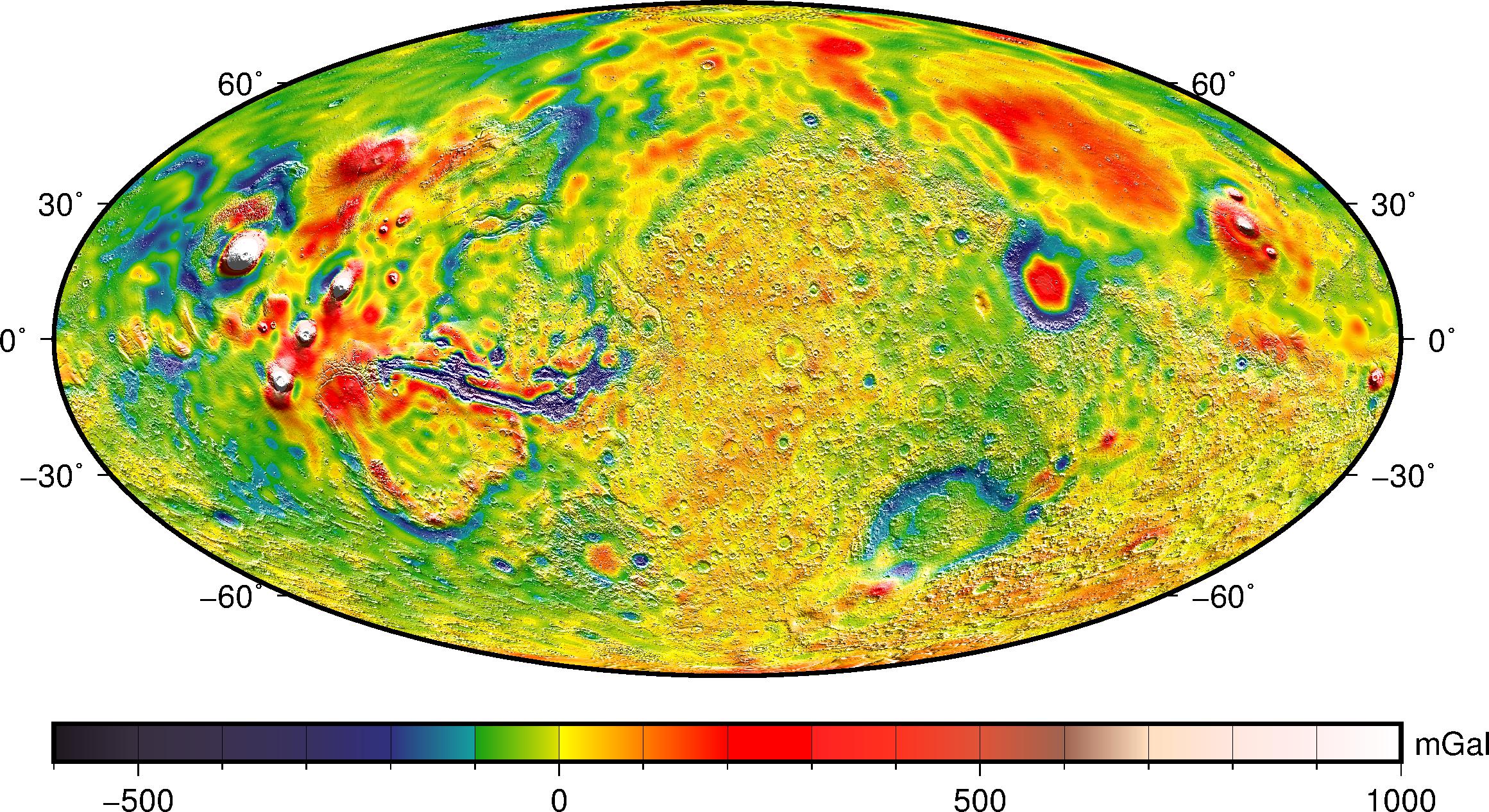
The Mars Gravity Model 2011 (MGM2011), showing variations of gravity accelerations over Mars’s surface. At just 0.376 of the Earth standard (or 0.376 g), a person who weighs 100 kg on Earth would weigh only 38 kg on Mars.

On top that, the gravity on Mars' surface is much lower than it is here on Earth – 62% lower to be precise. The average surface temperature is also lower on Mars, ranking in at a frigid -63 ☌ compared to Earth's balmy 14 ☌.Īnd while the length of a Martian day is roughly the same as it is here on Earth (24 hours 37 minutes), the length of a Martian year is significantly longer (687 days). For instance, atmospheric pressure on Mars is a tiny fraction of what it is here on Earth – averaging 7.5 millibars on Mars to just over 1000 here on Earth. The differences between Mars and Earth are all crucial for the existence of life as we know it. Understanding the effect this will likely have on human beings is of extreme importance when it comes time to send crewed missions to Mars, not to mention potential colonists.

One of these is the fact that gravity on Mars is just a fraction of what it is here on Earth. At the same time, our two planets are really quite different, and in a number of very important ways.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
